What is an Overbite?
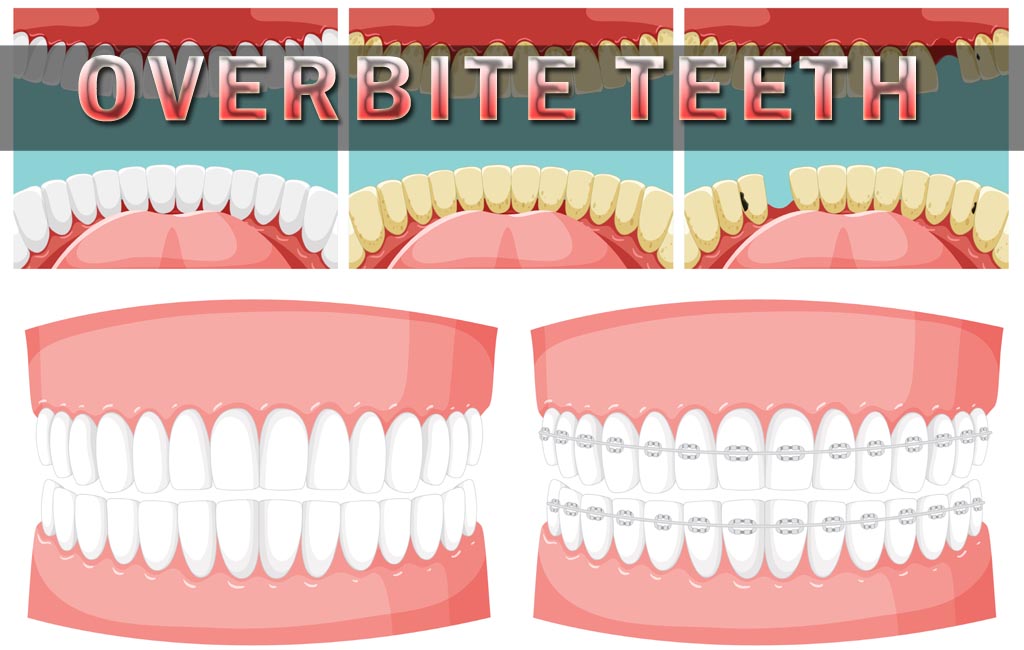
An overbite, sometimes referred to as a deep bite, occurs when the upper teeth extend too far over the lower teeth. Dentists differentiate between two main types of overbite: vertical and horizontal. A vertical overbite refers to the degree of overlap between the upper and lower teeth, while a horizontal overbite measures how far the upper teeth protrude in front of the lower teeth.
Normal overbite is usually around 2–3 millimeters. Anything beyond that can be considered a dental issue requiring attention. Overbite teeth can affect oral function, aesthetics, and even speech patterns if severe.
Causes of Overbite Teeth
Overbite teeth can develop due to several factors, often stemming from genetics, childhood habits, or jaw development problems. Key causes include:
- Genetics: Family history plays a significant role. If parents had overbite issues, children are more likely to develop them.
- Childhood habits: Prolonged thumb sucking, pacifier use, or bottle feeding can push upper teeth forward, creating an overbite.
- Jaw development issues: Disproportionate growth between the upper and lower jaw can cause teeth misalignment.
- Missing or misaligned teeth: Tooth loss or improperly aligned teeth can force other teeth out of position, contributing to an overbite.
Symptoms of Overbite Teeth
Recognizing the signs of overbite teeth is essential for early intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Upper teeth protruding significantly over lower teeth.
- Difficulty biting or chewing food efficiently.
- Speech difficulties, including lisping or mispronunciation.
- Jaw pain or discomfort due to uneven stress on the jaw joint.
- Worn enamel, tooth sensitivity, or increased risk of tooth decay.
Complications of Untreated Overbite
If overbite teeth are left untreated, they can lead to several oral health and medical issues:
- Tooth decay and gum disease: Misaligned teeth are harder to clean, increasing plaque buildup and cavities.
- TMJ disorders: Uneven stress on the jaw can lead to temporomandibular joint pain, headaches, and clicking sounds.
- Chronic headaches and jaw pain: Overbite teeth can strain facial muscles, causing persistent discomfort.
- Difficulty maintaining oral hygiene: Crowded or overlapping teeth make brushing and flossing challenging.
Diagnosis of Overbite Teeth
Diagnosis is performed by a dental professional or orthodontist through a combination of clinical examination and imaging. The process may include:
- Visual dental examination to assess bite and teeth alignment.
- X-rays or 3D imaging to evaluate jaw structure and tooth position.
- Assessment of jaw function, including chewing patterns and speech.
Early detection, especially in children, allows for interventions that can prevent severe overbite complications later in life.
Treatment Options for Overbite Teeth
Treating overbite teeth depends on the severity, age of the patient, and underlying cause. Popular treatment options include:
Orthodontic Treatments
- Braces: Traditional metal braces are effective in gradually correcting overbite by realigning teeth and jaw position.
- Clear aligners: Invisalign and similar products offer a discreet way to correct overbite, particularly in mild to moderate cases.
Dental Appliances
- Retainers: Used post-treatment to maintain corrected teeth position.
- Headgear: Helps in redirecting jaw growth in children and adolescents with severe overbite teeth.
Surgical Correction
For severe cases where orthodontic treatment alone is insufficient, corrective jaw surgery may be necessary. Surgery realigns the upper and lower jaw, allowing proper bite and improving facial aesthetics.
Early Intervention in Children
Intervening during childhood can prevent severe overbite development. Early treatments may include dental appliances, habit-correcting devices, and orthodontic guidance to ensure proper jaw growth.
Prevention Tips for Overbite Teeth
While genetics cannot be changed, several preventive measures can reduce the risk of developing overbite teeth:
- Discourage prolonged thumb sucking and pacifier use in children.
- Ensure early orthodontic consultations by age 7 to identify potential bite issues.
- Maintain regular dental check-ups for timely detection of misaligned teeth.
- Encourage proper oral hygiene habits to avoid secondary issues caused by misalignment.
Living with an Overbite
Even with overbite teeth, patients can maintain a healthy, functional, and attractive smile. Key considerations include:
- Regular dental cleanings and check-ups to prevent decay.
- Using mouthguards during sports to protect protruding teeth.
- Maintaining orthodontic appliances or retainers as prescribed.
- Cosmetic options such as veneers or bonding for minor aesthetic concerns.
Conclusion
Overbite teeth are a common dental condition that, if left untreated, can lead to functional problems and oral health complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options helps individuals take proactive steps toward correction. Early intervention, professional orthodontic guidance, and preventive measures are key to ensuring proper dental alignment and a healthy smile for life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Overbite Teeth
What exactly are overbite teeth?
Overbite teeth refer to a dental condition where the upper front teeth significantly overlap the lower front teeth. While a small overlap is normal, a pronounced overbite can affect chewing, speaking, and oral health.
What causes overbite teeth?
Overbite can develop due to genetics, childhood habits such as thumb sucking or prolonged pacifier use, jaw development issues, and misaligned or missing teeth.
Are overbite dangerous if left untreated?
Yes, untreated overbite can lead to complications like tooth decay, gum disease, jaw pain, temporomandibular joint disorders, and difficulty maintaining proper oral hygiene.
How can overbite be diagnosed?
Dentists or orthodontists diagnose overbite through visual examination, X-rays, and other imaging techniques to assess tooth alignment and jaw structure.
What treatments are available for overbite?
Treatment options for overbite teeth include braces, clear aligners, dental appliances like retainers or headgear, and in severe cases, surgical correction of the jaw.
Can overbite teeth be corrected in children?
Yes, early intervention in children can prevent severe overbite. Orthodontists can use appliances to guide jaw growth and correct tooth alignment before the bite becomes more pronounced.
Is it possible to prevent overbite teeth?
Preventive measures include discouraging thumb sucking and prolonged pacifier use, monitoring oral habits in children, and visiting the dentist regularly for early detection of misalignment.
How long does it take to fix overbite?
The duration of treatment for overbite depends on the severity. Mild cases may take a few months with clear aligners, while severe overbite may require braces or surgery for one to three years.
Can overbite teeth affect speech?
Yes, overbite can cause speech difficulties, including lisping or mispronunciation, especially if the overbite is severe and alters tongue placement while speaking.
What is life like after correcting overbite?
After correcting overbite, patients often experience improved oral function, better aesthetics, easier maintenance of oral hygiene, and reduced risk of complications like jaw pain and tooth wear.